Calculate the one temperature at which Fahrenheit and Kelvin thermometers agree with each other

Like the Kelvin scale, the Rankine scale is an absolute temperature scale: Absolute zero is zero degrees Rankine (0°R). However, the units of this scale are the same size as those of the Fahrenheit scale rather than the Celsius scale. What is the numerical value of the triple-point temperature of water on the Rankine scale?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
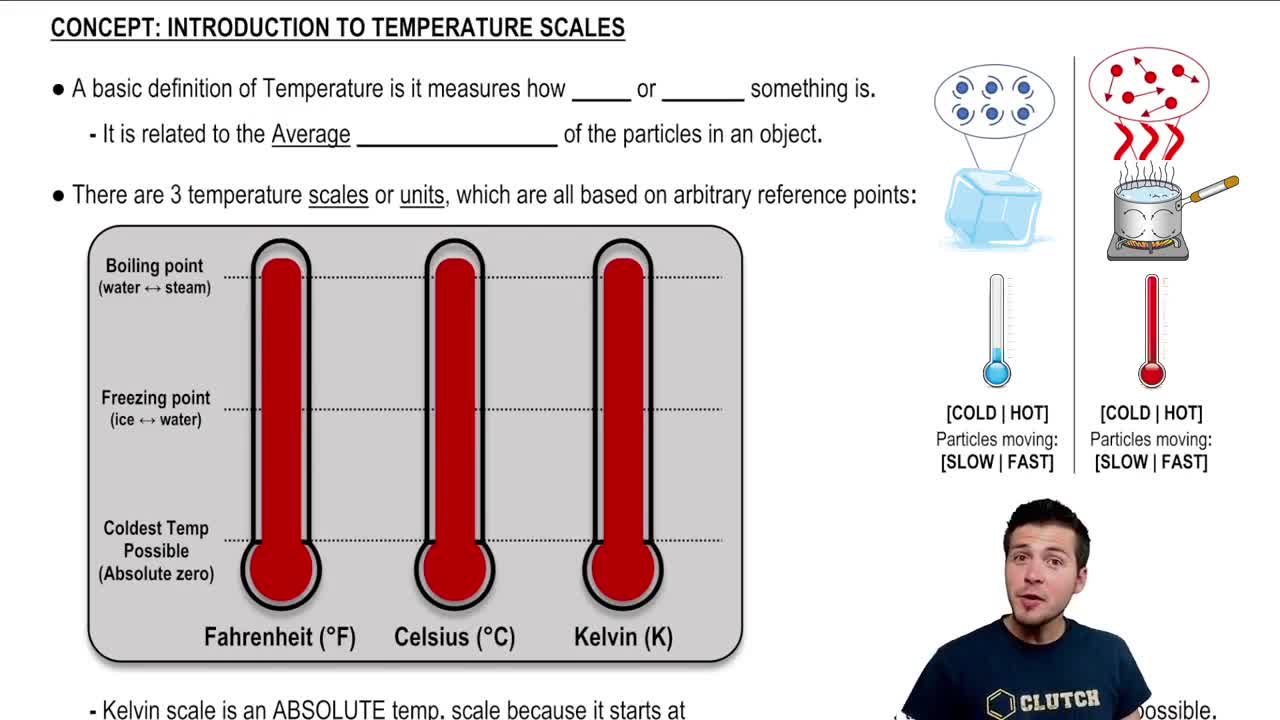
Key Concepts
Absolute Temperature Scale
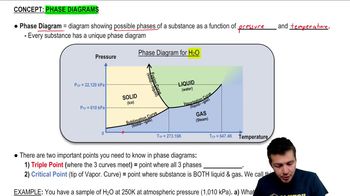
Triple Point of Water
Temperature Conversion

The pressure of a gas at the triple point of water is atm. If its volume remains unchanged, what will its pressure be at the temperature at which CO2 solidifies?
A constant-volume gas thermometer registers an absolute pressure corresponding to mm of mercury when in contact with water at the triple point. What pressure does it read when in contact with water at the normal boiling point?
One of the tallest buildings in the world is the Taipei 101 in Taiwan, at a height of 1671 feet. Assume that this height was measured on a cool spring day when the temperature was 15.5°C. You could use the building as a sort of giant thermometer on a hot summer day by carefully measuring its height. Suppose you do this and discover that the Taipei 101 is 0.471 foot taller than its official height. What is the temperature, assuming that the building is in thermal equilibrium with the air and that its entire frame is made of steel?
A geodesic dome constructed with an aluminum framework is a nearly perfect hemisphere; its diameter measures 55.0 m on a winter day at a temperature of -15°C. How much more interior space does the dome have in the summer, when the temperature is 35°C?
A 6.00-kg piece of solid copper metal at an initial temperature T is placed with 2.00 kg of ice that is initially at -20.0°C. The ice is in an insulated container of negligible mass and no heat is exchanged with the surroundings. After thermal equilibrium is reached, there is 1.20 kg of ice and 0.80 kg of liquid water. What was the initial temperature of the piece of copper?
