Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
c. The visceral motor division is also known as the autonomic nervous system and maintains homeostasis of many physiological variables.

 Erin C. Amerman 2nd Edition
Erin C. Amerman 2nd Edition Ch. 14 The Autonomous Nervous System and Homeostasis
Ch. 14 The Autonomous Nervous System and Homeostasis Problem 3
Problem 3 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

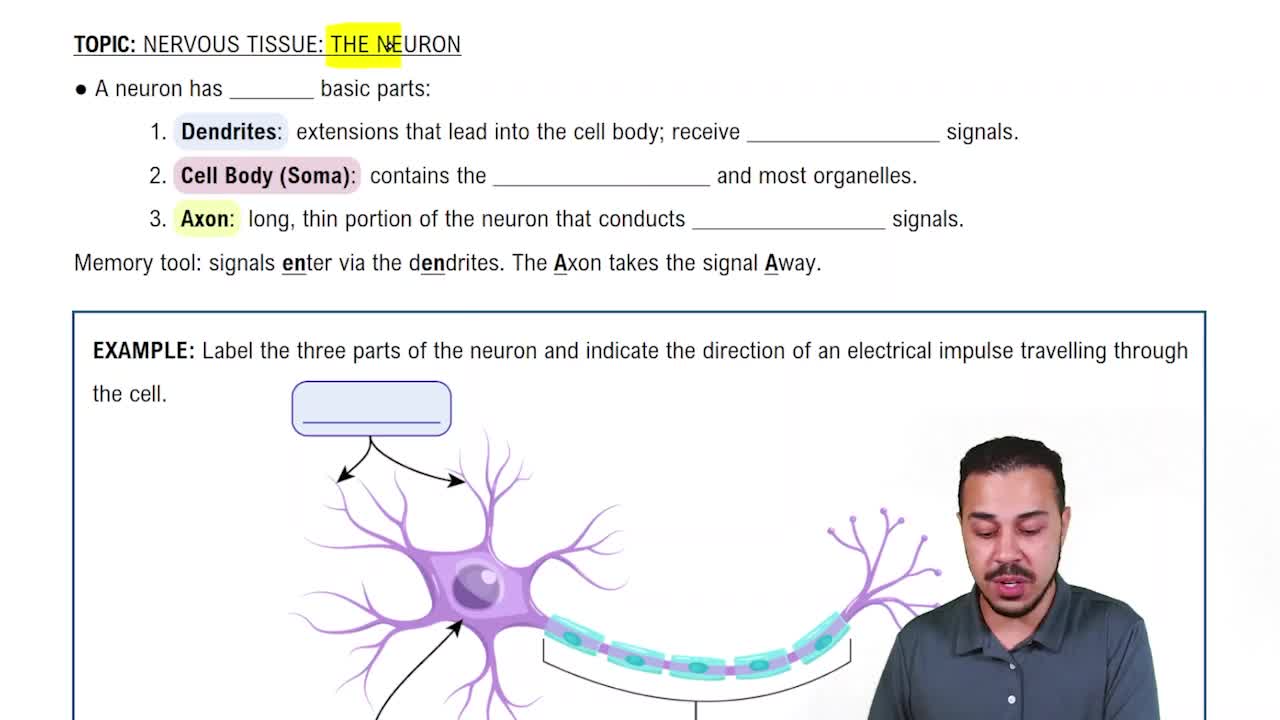

Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
c. The visceral motor division is also known as the autonomic nervous system and maintains homeostasis of many physiological variables.
Regulation of heart rate, blood pressure, and digestive functions is carried out by the:
a. Somatic motor division of the peripheral nervous system.
b. Central nervous system.
c. Visceral sensory division of the peripheral nervous system.
d. Autonomic nervous system.
The sympathetic nervous system is also known as the ________ division because the cell bodies of its preganglionic neurons are located in the ________ .
Differentiate between adrenergic and cholinergic receptors.
Which neurotransmitter(s) is/are used by sympathetic postganglionic neurons?
a. Epinephrine
b. Norepinephrine
c. Acetylcholine
d. Both a and b
e. All of the above
Explain what happens when sympathetic neurons stimulate the adrenal medulla. What purpose does this serve?