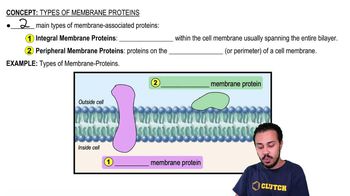
In what way do the membranes of a eukaryotic cell vary?
a. Phospholipids are found only in certain membranes.
b. Certain proteins are unique to each membrane.
c. Only certain membranes of the cell are selectively permeable.
d. Only certain membranes are constructed from amphipathic molecules.