In eukaryotes, what allows only certain genes to be expressed in different types of cells?

Compare and contrast the items in each pair:
(b) promoter-proximal elements and the operator of the lac operon
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Promoter-Proximal Elements
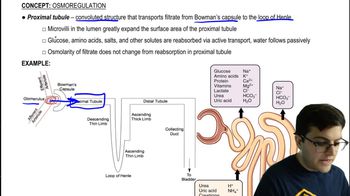
Operator of the Lac Operon
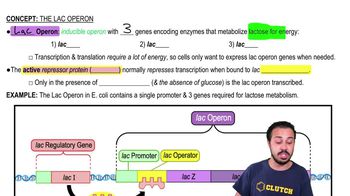
Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes

What is alternative splicing?
a. Phosphorylation that leads to different types of post-translational regulation
b. mRNA processing that leads to different combinations of exons being spliced together
c. Folding that leads to proteins with alternative conformations
d. The outcome of regulatory proteins that leads to changes in the life span of an mRNA
Compare and contrast the items in each pair:
(a) enhancers and the E. coli CAP binding site
Compare and contrast the items in each pair:
(c) general transcription factors and sigma.
Imagine discovering a loss-of-function mutation in a eukaryotic gene. You determine the gene's nucleotide sequence from the start site for transcription to the termination point of transcription and find no differences from the wild-type sequence. Explain where you think the mutation might be and how the mutation might be acting.
The following statements are about the control of chromatin condensation. Select True or False for each.
T/F Reducing histone acetylase activity is likely to decrease gene transcription.
T/F Mutations that reduce the number of positively charged amino acids on histones should promote open chromatin.
T/F Chromatin remodeling complexes add chemical groups to histones.
T/F Adding an inhibitor of DNA methylation is likely to reduce gene transcription.
