Ch. 26 - Bacteria and Archaea

Chapter 26, Problem 16
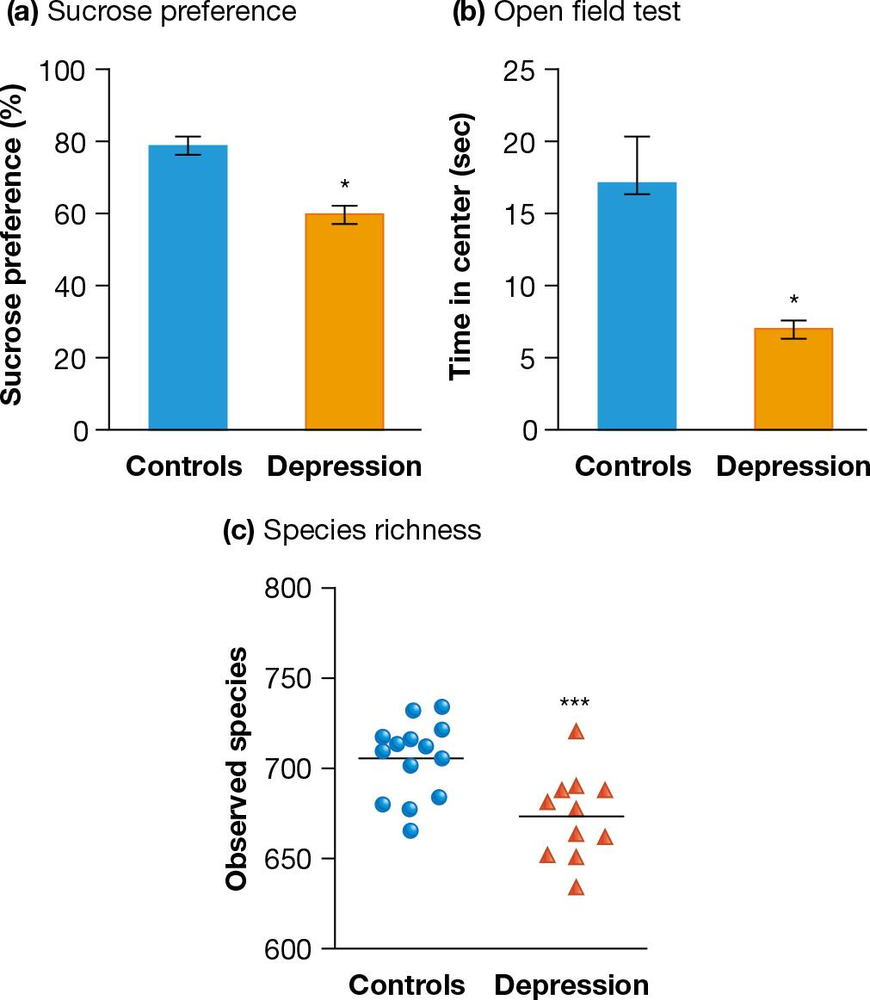
Researchers examined the relationship between gut microbiomes and depression. To do so, they collected fecal samples from people with depression and also a control group of individuals with no signs of depression. They then performed a fecal microbiota transfer (FMT) by adding the samples to rats that had no gut microbiota and examined behaviors associated with depression and anxiety as well as species of bacteria that ended up growing in the rats’ guts. The results are presented below. Graph (a) shows the rats’ interest in a pleasurable experience (drinking sugar water). Graph (b) shows the amount of time rats spent out in the open versus along the edge of an area (a sign of anxiety). Graph (c) shows the number of species observed in rats after FMT.
Probiotics are often marketed as a food or supplement that can help promote a healthy gut. How might a healthy gut microbiome help improve mental health?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Examine Graph (a) which shows the sucrose preference test. Note that rats with fecal samples from depressed individuals show a lower preference for sucrose compared to controls, indicating anhedonia, a symptom of depression.
Analyze Graph (b) which depicts the open field test. Observe that rats with fecal samples from depressed individuals spend less time in the center of the field, indicating higher anxiety levels compared to controls.
Look at Graph (c) which shows species richness. Notice that the number of observed species in the gut microbiota of rats with fecal samples from depressed individuals is lower compared to controls.
Consider how a healthy gut microbiome might influence mental health. A diverse and balanced gut microbiome can produce neurotransmitters and other metabolites that influence brain function and mood.
Reflect on the potential role of probiotics. Probiotics can help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiome, potentially improving mental health by reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety through the gut-brain axis.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome refers to the diverse community of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract. These microbes play a crucial role in digestion, metabolism, and immune function. Recent research suggests that the gut microbiome can influence mental health by producing neurotransmitters and other metabolites that affect brain function and mood regulation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The Human Microbiome
Fecal Microbiota Transfer (FMT)
Fecal microbiota transfer (FMT) is a medical procedure that involves transferring fecal matter from a healthy donor to a recipient to restore a balanced gut microbiome. This technique has been studied for its potential to treat various conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders and, as indicated in the question, mental health issues like depression, by altering the microbial composition in the recipient's gut.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Horizontal Gene Transfer
Behavioral Indicators of Mental Health
Behavioral indicators of mental health, such as sucrose preference and open field test results, are used to assess mood and anxiety levels in animal models. A decreased preference for sucrose can indicate anhedonia, a common symptom of depression, while reduced time spent in the center of an open field suggests increased anxiety. These behaviors help researchers evaluate the impact of gut microbiome changes on mental health.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Behavior
Related Practice
