The accompanying image shows photoluminescence from four different samples of CdTe nanocrystals, each embedded in a polymer matrix. The photoluminescence occurs because the samples are being irradiated by a UV light source. The nanocrystals in each vial have different average sizes. The sizes are 4.0, 3.5, 3.2, and 2.8 nm. (a) Which vial contains the 4.0-nm nanocrystals?
Ch.12 - Solids and Modern Materials

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 12, Problem 12b
Silicon is the fundamental component of integrated circuits. Si has the same structure as diamond. (b) Silicon readily reacts to form silicon dioxide, SiO2, which is quite hard and is insoluble in water. Is SiO2 most likely a molecular, metallic, ionic, or covalent-network solid?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the types of solids: molecular, metallic, ionic, and covalent-network.
Consider the properties of SiO2: it is hard and insoluble in water.
Recall that molecular solids are typically soft and have low melting points, which does not match SiO2.
Metallic solids are characterized by metallic bonding and conductivity, which does not apply to SiO2.
Covalent-network solids are hard, have high melting points, and are insoluble in water, which matches the properties of SiO2.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
50sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Types of Solids
Solids can be classified into different categories based on their bonding and structure. Molecular solids consist of molecules held together by intermolecular forces, metallic solids are composed of metal atoms sharing electrons, ionic solids are formed from the electrostatic attraction between ions, and covalent-network solids feature a continuous network of covalent bonds. Understanding these categories helps in predicting the properties of materials.
Recommended video:
Guided course
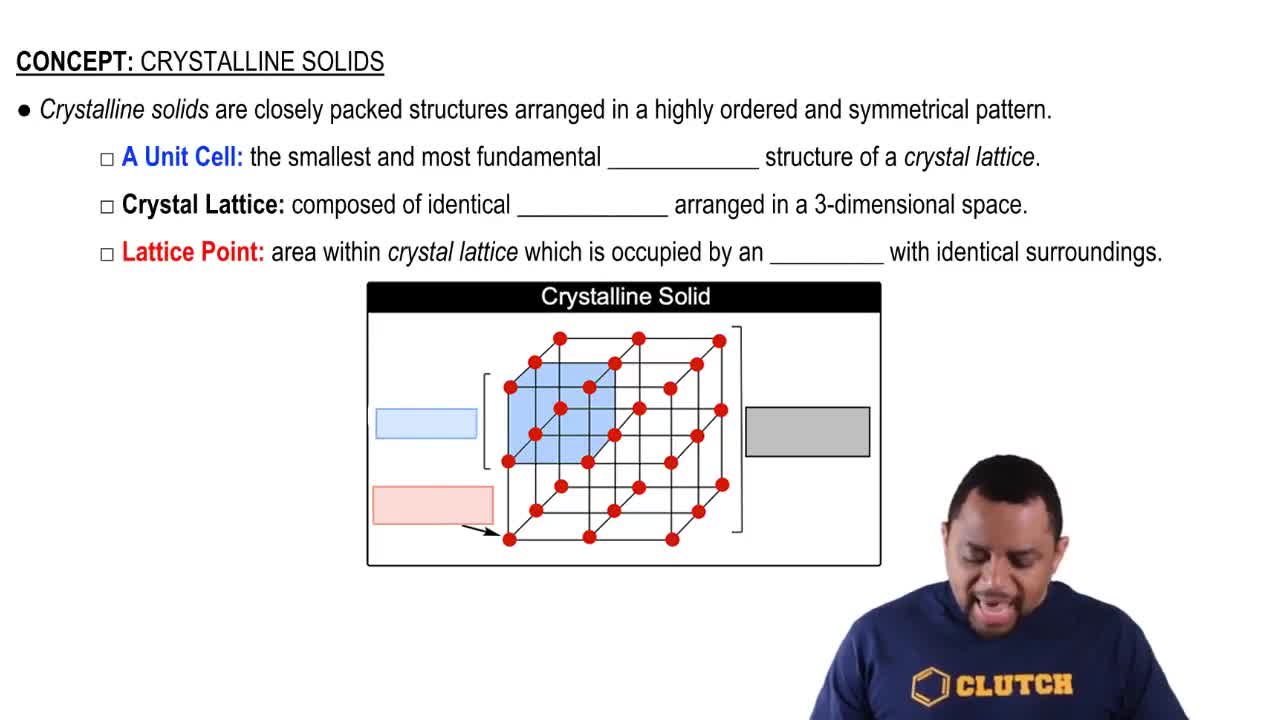
Crystalline Solids Structure
Silicon Dioxide Structure
Silicon dioxide (SiO2) has a three-dimensional network structure where each silicon atom is covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms, and each oxygen atom is bonded to two silicon atoms. This arrangement creates a strong, rigid lattice that contributes to its hardness and insolubility in water. Recognizing this structure is crucial for identifying SiO2 as a covalent-network solid.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Resonance Structures
Properties of Covalent-Network Solids
Covalent-network solids, like SiO2, exhibit unique properties such as high melting points, hardness, and low electrical conductivity. These properties arise from the strong covalent bonds that extend throughout the material, making them very stable. Understanding these characteristics is essential for determining the classification of SiO2 in the context of solid-state chemistry.
Recommended video:
Guided course
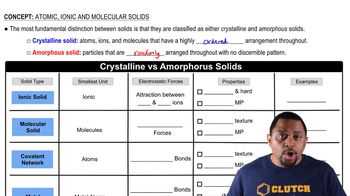
Crystalline vs Amorphous Solids
Related Practice
Textbook Question
268
views
Textbook Question
Silicon is the fundamental component of integrated circuits. Si has the same structure as diamond. (a) Is Si a molecular, metallic, ionic, or covalent-network solid?
354
views
Textbook Question
What kinds of attractive forces exist between particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) in (a) molecular crystals?
1166
views
Textbook Question
What kinds of attractive forces exist between particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) in (d) and metallic crystals?
519
views
Textbook Question
Which type (or types) of crystalline solid is characterized by each of the following? (a) High mobility of electrons throughout the solid;
1063
views
