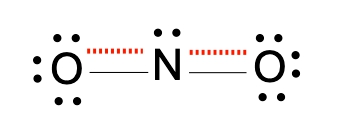
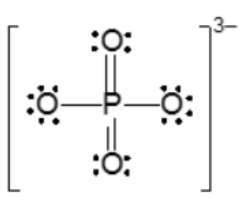
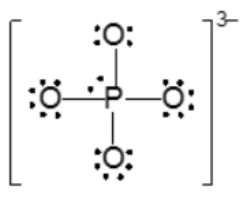
Resonance structures are essential in understanding the behavior of molecules with pi bonds, particularly in polyatomic ions. They consist of two or more valid Lewis structures that depict the same arrangement of atoms but differ in the placement of electrons, specifically pi bonds or lone pairs. For instance, the nitride ion can be represented by two resonance structures where the pi bond is alternately placed on the left or right oxygen atom. Both representations are valid and illustrate the concept of resonance.
To indicate these resonance structures, double-sided arrows are used, signifying that the structures are equivalent. At an introductory level, it is acceptable to consider these resonance structures as equal; however, in more advanced studies, such as organic chemistry, it becomes clear that not all resonance structures hold the same significance or stability.
The actual structure of the molecule is best represented by a resonance hybrid, which is a composite of all major resonance structures. This hybrid reflects an average of the contributing structures. To illustrate the resonance hybrid, dotted lines are employed to indicate the presence of pi bonds that are delocalized across the molecule. For the nitride ion, dotted lines would be drawn where the pi bonds were originally located, effectively capturing the essence of the resonance hybrid.