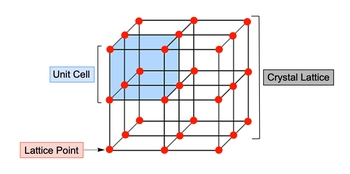
Crystalline solids are characterized by their closely packed structures, which are arranged in a highly ordered and symmetrical pattern. Understanding the fundamental components of these solids is essential for grasping their properties and behaviors. Three key terms are crucial in this context: unit cell, crystal lattice, and lattice points.
A unit cell is defined as the smallest and most fundamental repeating structure of a crystal lattice. It serves as the building block from which the entire crystal structure is formed. The crystal lattice itself consists of identical unit cells arranged in three-dimensional space, creating the overall framework of the crystalline solid.
Within this lattice, lattice points represent specific locations occupied by atoms, each surrounded by identical environments. For instance, if we visualize a crystalline solid as a structure made up of eight stacked cubes, the entire assembly represents the crystal lattice. Each individual cube corresponds to a unit cell, while the edges and corners of these cubes denote the lattice points.
In summary, when examining crystalline solids, it is helpful to consider the macro view of the entire structure alongside the micro view of the unit cell and lattice points. This layered understanding enhances comprehension of the intricate organization within crystalline materials.