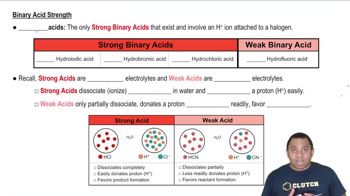
Ionization of Acids
The ionization of acids refers to the process by which an acid donates protons to water, resulting in the formation of hydronium ions (H₃O⁺) and conjugate bases. For diprotic acids, this process occurs in two stages, each with its own equilibrium constant (Ka). Understanding this concept is crucial for predicting the behavior of diprotic acids in solution and their relative strengths.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance