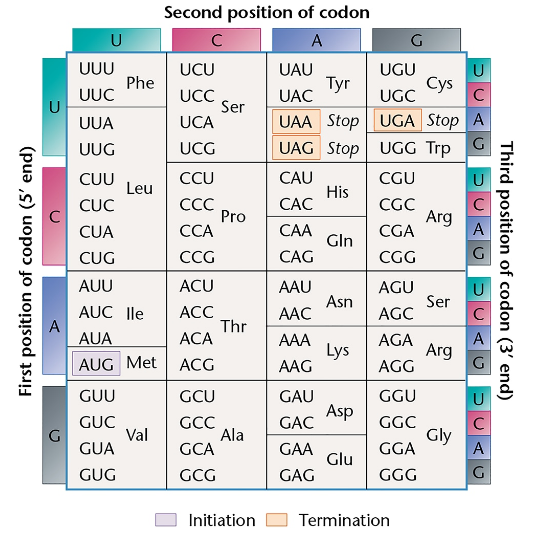
A short RNA molecule was isolated that demonstrated a hyperchromic shift, indicating secondary structure. Its sequence was determined to be
5'-AGGCGCCGACUCUACU-3'
If the molecule were a tRNA fragment containing a CGA anticodon, what would the corresponding codon be?