How do we know that the orientation of promoters relative to the transcription start site is important while enhancers are orientation independent?
Ch. 17 - Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes

Chapter 17, Problem 2
Write a short essay describing how cis-acting regulatory elements, activators, and chromatin modifiers are all coordinately involved in regulating transcription initiation.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by defining cis-acting regulatory elements as DNA sequences located near the gene they regulate, such as promoters and enhancers, which serve as binding sites for proteins that control transcription initiation.
Explain that activators are proteins that bind to these cis-acting elements to increase the rate of transcription by facilitating the assembly of the transcription machinery at the promoter.
Describe chromatin modifiers as enzymes or protein complexes that alter the structure of chromatin (e.g., through histone acetylation or methylation), thereby changing the accessibility of DNA to transcription factors and RNA polymerase.
Discuss how these three components work together: cis-acting elements provide specific binding sites, activators recognize and bind these sites to recruit or stabilize the transcriptional machinery, and chromatin modifiers remodel chromatin to create a more open or closed environment for transcription initiation.
Conclude by emphasizing that the coordinated interaction among cis-acting elements, activators, and chromatin modifiers ensures precise spatial and temporal control of gene expression, allowing cells to respond dynamically to internal and external signals.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cis-acting Regulatory Elements
Cis-acting regulatory elements are DNA sequences located near or within a gene that control its transcription. These include promoters, enhancers, and silencers, which serve as binding sites for transcription factors and other proteins, influencing the rate and timing of gene expression.
Recommended video:
Guided course
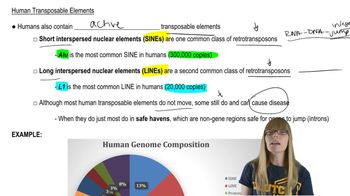
Human Transposable Elements
Activators
Activators are proteins that bind to specific cis-acting elements, such as enhancers, to increase transcription. They facilitate the recruitment of the transcriptional machinery, including RNA polymerase II, often by interacting with coactivators and the basal transcription complex.
Recommended video:
Guided course
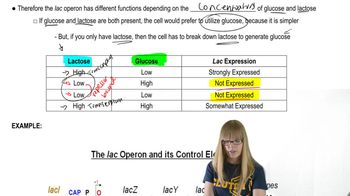
Lac Operon Summary
Chromatin Modifiers
Chromatin modifiers are enzymes that alter chromatin structure through chemical modifications like acetylation or methylation of histones. These changes can either relax or compact chromatin, thereby regulating the accessibility of DNA to transcription factors and RNA polymerase, and ultimately controlling transcription initiation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chromatin
Related Practice
Textbook Question
612
views
Textbook Question
How do we know that eukaryotic transcription factors bind to DNA sequences at or near promoter regions?
476
views
Textbook Question
How do we know that there is an association between disease susceptibility in humans and regulatory DNA sequences?
408
views
Textbook Question
What features of eukaryotes provide additional opportunities for the regulation of gene expression compared to bacteria?
853
views
Textbook Question
Provide a definition of chromatin remodeling, and give two examples of this phenomenon.
681
views
Textbook Question
Describe the organization of the interphase nucleus. Include in your presentation a description of chromosome territories, interchromatin compartments, and transcription factories.
706
views
