Textbook Question
What role do the following cellular components play in the storage, expression, or transmission of genetic information?
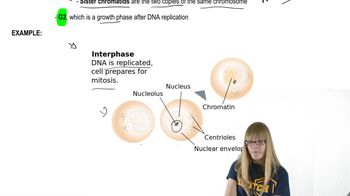
(a) Chromatin
(b) Nucleolus
(c) Ribosome
(d) Mitochondrion
(e) Centriole
(f) Centromere
844
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

What role do the following cellular components play in the storage, expression, or transmission of genetic information?
(a) Chromatin
(b) Nucleolus
(c) Ribosome
(d) Mitochondrion
(e) Centriole
(f) Centromere
Discuss the concepts of homologous chromosomes, diploidy, and haploidy. What characteristics do two homologous chromosomes share?
If two chromosomes of a species are the same length and have similar centromere placements and yet are not homologous, what is different about them?
How are chromosomes named on the basis of their centromere placement?
Contrast telophase in plant and animal mitosis.
Describe the phases of the cell cycle and the events that characterize each phase.