Datura stramonium (the Jimsonweed) expresses flower colors of purple and white and pod textures of smooth and spiny. The results of two crosses in which the parents were not necessarily true breeding are shown below. Assuming that true-breeding strains of all combinations of traits are available, what single cross could you execute and carry to an F₂ generation that will prove or disprove your hypothesis? Assuming your hypothesis is correct, what results of this cross will support it?

To assess Mendel's law of segregation using tomatoes, a true-breeding tall variety (SS) is crossed with a true-breeding short variety (ss). The heterozygous F₁ tall plants (Ss) were crossed to produce two sets of F₂ data, as follows.
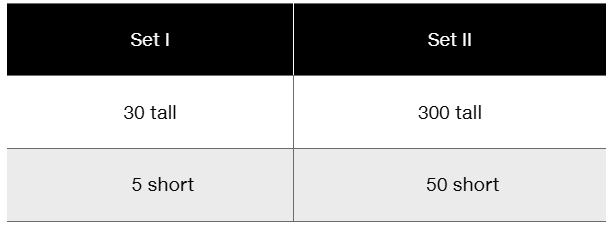
Using the X² test, analyze the results for both datasets. Calculate X² values and estimate the p values in both cases.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Mendel's Law of Segregation

Chi-Square (X²) Test

p-Value and Statistical Significance

The wild-type (normal) fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, has straight wings and long bristles. Mutant strains have been isolated that have either curled wings or short bristles. The genes representing these two mutant traits are located on separate chromosomes. Carefully examine the data from the following five crosses.
Identify each mutation as either dominant or recessive. In each case, indicate which crosses support your answer.
The wild-type (normal) fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, has straight wings and long bristles. Mutant strains have been isolated that have either curled wings or short bristles. The genes representing these two mutant traits are located on separate chromosomes. Carefully examine the data from the following five crosses.
Assign gene symbols and, for each cross, determine the genotypes of the parents.
To assess Mendel's law of segregation using tomatoes, a true-breeding tall variety (SS) is crossed with a true-breeding short variety (ss). The heterozygous F₁ tall plants (Ss) were crossed to produce two sets of F₂ data, as follows.
From the above analysis, what can you conclude about the importance of generating large datasets in experimental conditions?
Albinism, caused by a mutational disruption in melanin (skin pigment) production, has been observed in many species, including humans. In 1991, and again recently in 2017, the only documented observations of an albino humpback whale (named 'Migaloo') were observed near New South Wales. Recently, Polanowski and coworkers (Polanowski, A., S. Robinson-Laverick, and D. Paton. (2012). Journal of Heredity 103:130–133) studied the genetics of humpback whales from the east coast of Australia, including Migaloo. Do you think that Migaloo's albinism is more likely caused by a dominant or recessive mutation? Explain your reasoning.
Albinism, caused by a mutational disruption in melanin (skin pigment) production, has been observed in many species, including humans. In 1991, and again recently in 2017, the only documented observations of an albino humpback whale (named 'Migaloo') were observed near New South Wales. Recently, Polanowski and coworkers (Polanowski, A., S. Robinson-Laverick, and D. Paton. (2012). Journal of Heredity 103:130–133) studied the genetics of humpback whales from the east coast of Australia, including Migaloo. What data would be helpful in determining the answer to part (a)?
