Solution A has a pH of 4.0, and solution B has a pH of 6.0.
a. Which solution is more acidic?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
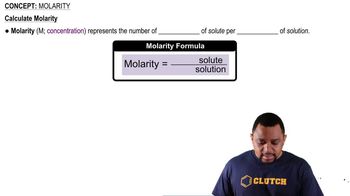


Solution A has a pH of 4.0, and solution B has a pH of 6.0.
a. Which solution is more acidic?
Solution X has a pH of 9.0, and solution Y has a pH of 7.0.
a. Which solution is more acidic?
A 0.205 M NaOH solution is used to titrate 20.0 mL of a solution of H2SO4. If 45.6 mL of the NaOH solution is required to reach the endpoint, what is the molarity of the H2SO4 solution?
H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → 2H2O(l) + Na2SO4
A buffer solution is made by dissolving H3PO4 and NaH2PO4 in water.
a. Write an equation that shows how this buffer neutralizes added acid.
A buffer solution is made by dissolving H3PO4 and NaH2PO4 in water.
b. Write an equation that shows how this buffer neutralizes added base.
Determine each of the following for a 0.050 M KOH solution:
a. [H3O+]