Textbook Question
Indicate whether each of the following statements is characteristic of an acid, a base, or both
a. has a sour taste
951
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
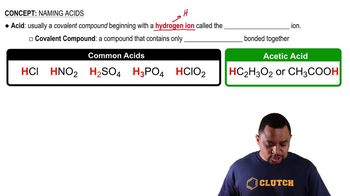

Indicate whether each of the following statements is characteristic of an acid, a base, or both
a. has a sour taste
Indicate whether each of the following statements is characteristic of an acid, a base, or both
c. produces H⁺ ions in water
Indicate whether each of the following statements is characteristic of an acid, a base, or both
d. is named barium hydroxide
Indicate whether each of the following statements is characteristic of an acid, a base, or both
e. is an electrolyte