Write a balanced equation for the neutralization of each of the following:
c. HNO3(aq) and Mg(OH)2(s)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

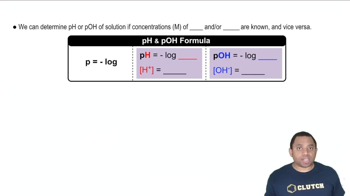
Write a balanced equation for the neutralization of each of the following:
c. HNO3(aq) and Mg(OH)2(s)
If 32.8 mL of a 0.162 M NaOH solution is required to titrate 25.0 mL of a solution of H2SO4, what is the molarity of the H2SO4 solution?
H2SO4(aq) + 2 KOH(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + K2SO4(aq)
Which of the following represents a buffer system? Explain.
a. H3PO3
b. NaNO3
c. HC2H3O2 and NaC2H3O2
d. HCl and NaOH
When food enters the stomach, HCl is released and the [H3O+] of the stomach fluid rises to 4 × 10–2 M. What is the pH of the stomach fluid?
Write the balanced chemical equation for the neutralization reaction of stomach acid HCl with Al(OH)3, an ingredient in some antacids.
How many grams of Al(OH)3 are required to neutralize 150. mL of stomach acid with a pH of 1.5?