Textbook Question
What are the kind and number of atoms in the ring portion of the Haworth structure of glucose?
1305
views

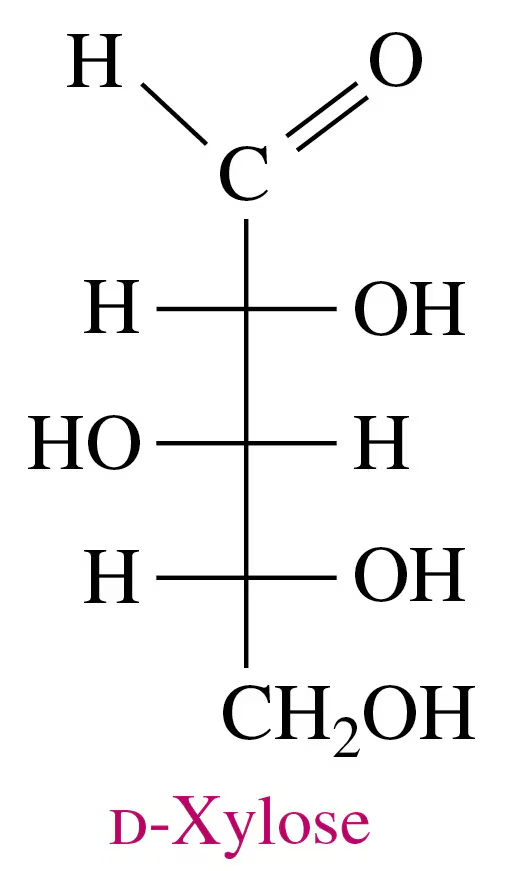
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



What are the kind and number of atoms in the ring portion of the Haworth structure of glucose?
Draw the Haworth structures for α- and ß-D-glucose.
Identify each of the following as the α or ß isomer:
a.
Draw the Fischer projection for the oxidation and the reduction products of D-mannose. What are the names of the sugar acid and the sugar alcohol produced?
Draw the Fischer projection for the oxidation and the reduction products of D-arabinose. What are the names of the sugar acid and the sugar alcohol produced?
For each of the following, give the monosaccharide units produced by hydrolysis, the type of glycosidic bond, and the name of the disaccharide, including α or β:
a.