Textbook Question
D-Fructose is the sweetest monosaccharide. How does the Fischer projection of D-fructose differ from that of D-glucose?
625
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
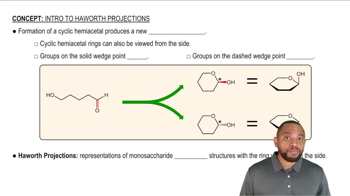


D-Fructose is the sweetest monosaccharide. How does the Fischer projection of D-fructose differ from that of D-glucose?
Identify the monosaccharide that fits each of the following descriptions:
a. is also called blood sugar
Identify a monosaccharide that fits each of the following descriptions:
a. found in high blood levels in diabetes
Draw the Haworth structures for α- and ß-D-glucose.
Identify each of the following as the α or ß isomer:
a.
Draw the Fischer projection for the oxidation and the reduction products of D-xylose. What are the names of the sugar acid and the sugar alcohol produced?