Textbook Question
Identify each of the following as a fatty acid, soap, triacylglycerol, wax, glycerophospholipid, sphingolipid, or steroid:
b. cholesterol
1198
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


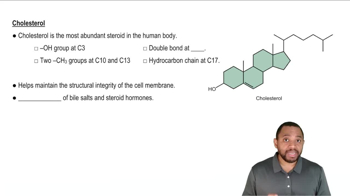
Identify each of the following as a fatty acid, soap, triacylglycerol, wax, glycerophospholipid, sphingolipid, or steroid:
b. cholesterol
Identify each of the following as a fatty acid, soap, triacylglycerol, wax, glycerophospholipid, sphingolipid, or steroid:
d. glyceryl tripalmitate (tripalmitin)
Identify the components (1 to 6) contained in each of the following lipids (a to d):
1. glycerol
2. fatty acid
3. phosphate
4. amino alcohol
5. steroid nucleus
6. sphingosine
d. triacylglycerol
Which of the following are found in cell membranes?
a. cholesterol
b. triacylglycerols
c. carbohydrates
Which of the following are found in cell membranes?
a. proteins
b. waxes
c. phospholipids