Seeds and vegetables are often deficient in one or more essential amino acids. Using the table in problem 16.63, state whether each combination provides all of the essential amino acids.
<IMAGE>
a. rice and lima beans

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
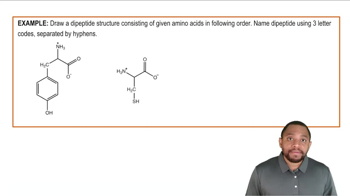
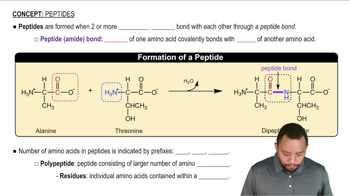
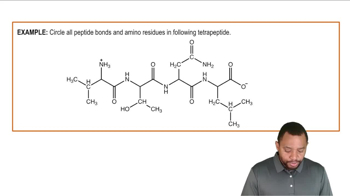
Seeds and vegetables are often deficient in one or more essential amino acids. Using the table in problem 16.63, state whether each combination provides all of the essential amino acids.
<IMAGE>
a. rice and lima beans
Seeds and vegetables are often deficient in one or more essential amino acids. Using the table in problem 16.63, state whether each combination provides all of the essential amino acids.
<IMAGE>
c. oatmeal and lima beans
What are some differences between each of the following pairs?
c. polar and nonpolar amino acids
What are some differences between each of the following pairs?
b. an ⍺ helix and collagen
If glutamate were replaced by proline in a protein, how might the tertiary structure be affected?
How do enzymes differ from catalysts used in chemical laboratories?