Textbook Question
What nucleic acid subunits are connected in a phosphodiester linkage in a polynucleotide?
591
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
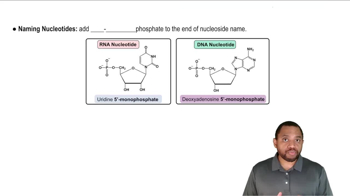

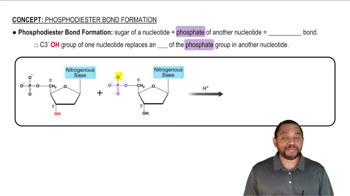
What nucleic acid subunits are connected in a phosphodiester linkage in a polynucleotide?
What components join together to form the backbone of a nucleic acid?
What component in a nucleic acid determines the 5' free end?
List three structural characteristics of DNA.
How are the two strands of nucleic acid in DNA held together?
Write the base sequence in a complementary DNA segment if each original segment has the following base sequence:
d. C T G T A T A C G T T A