Textbook Question
State whether each of the following components is present in DNA only, RNA only, or both DNA and RNA:
c. uracil
569
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

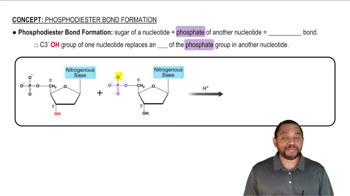
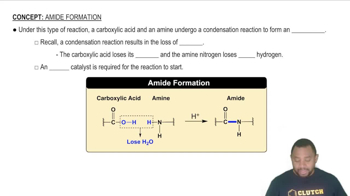
State whether each of the following components is present in DNA only, RNA only, or both DNA and RNA:
c. uracil
In the genetic disease uridine monophosphate synthase deficiency, symptoms include anemia, cardiac malformations, and infections. Draw the condensed structural formula for uridine monophosphate.
A deficiency of the enzyme adenine transferase causes a lack of adenine for purine synthesis and a high level of adenine in the urine. Draw the condensed structural formula for adenosine monophosphate.
What components join together to form the backbone of a nucleic acid?
What component in a nucleic acid determines the 5' free end?
Draw the condensed structural formula for the dinucleotide G C that would be in RNA.