Textbook Question
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleosides:
c. cytidine
579
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
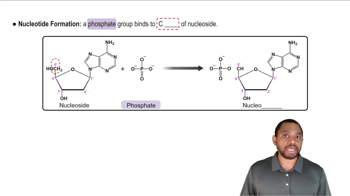


Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleosides:
c. cytidine
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
b. dAMP
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
d. UMP
Draw the condensed structural formula for CMP.
What is similar about the primary structure of RNA and DNA?
If the DNA double helix in salmon contains 28% adenine, what is the percentage of thymine, guanine, and cytosine?