Calculate each of the following temperatures in kelvins and degrees Fahrenheit:
b. The lowest recorded temperature in the world was –89.2 °C in Vostok, Antarctica, on July 21, 1983.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Calculate each of the following temperatures in kelvins and degrees Fahrenheit:
b. The lowest recorded temperature in the world was –89.2 °C in Vostok, Antarctica, on July 21, 1983.
What is –15 °F in degrees Celsius and in kelvins?
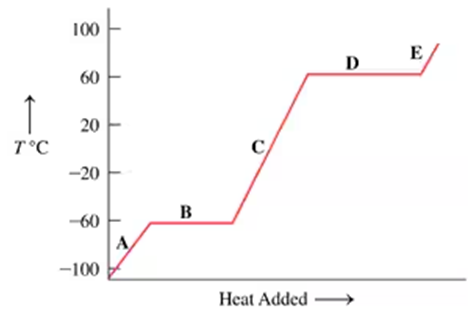
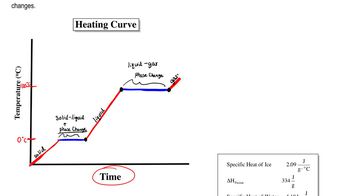
On a hot day, the beach sand gets hot but the water stays cool. Would you predict that the specific heat of sand is higher or lower than that of water? Explain.
<IMAGE>
A hot-water bottle for a patient contains 725 g of water at 65 °C. If the water cools to body temperature (37 °C), how many kilojoules of heat could be transferred to sore muscles?
When a 0.66-g sample of olive oil is burned in a calorimeter, the heat released increases the temperature of 370 g of water from 22.7 °C to 38.8 °C. What is the energy value for the olive oil in kcal/g?
A 45-g piece of ice at 0.0 °C is added to a sample of water at 8.0 °C. All of the ice melts and the temperature of the water decreases to 0.0 °C. How many grams of water were in the sample?