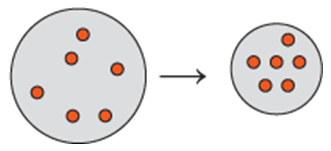
Indicate which diagram (1, 2, or 3) represents the volume of the gas sample in a flexible container when each of the following changes (a to d) takes place:
d. Doubling the atmospheric pressure and doubling the Kelvin temperature.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Indicate which diagram (1, 2, or 3) represents the volume of the gas sample in a flexible container when each of the following changes (a to d) takes place:
d. Doubling the atmospheric pressure and doubling the Kelvin temperature.
A balloon is filled with helium gas with a partial pressure of 1.00 atm and neon gas with a partial pressure of 0.50 atm. For each of the following changes (a to e) of the initial balloon, select the diagram (A, B, or C) that shows the final volume of the balloon:
<IMAGE>
c. All of the neon gas is removed (T and P do not change).
A balloon is filled with helium gas with a partial pressure of 1.00 atm and neon gas with a partial pressure of 0.50 atm. For each of the following changes (a to e) of the initial balloon, select the diagram (A, B, or C) that shows the final volume of the balloon:
<IMAGE>
d. The Kelvin temperature doubles and half of the gas atoms leak out (P does not change).
At a restaurant, a customer chokes on a piece of food. You put your arms around the person's waist and use your fists to push up on the person's abdomen, an action called the Heimlich maneuver.
b. Why does it cause the person to expel the food item from the airway?
In 1783, Jacques Charles launched his first balloon filled with hydrogen gas, which he chose because it was lighter than air. If the balloon had a volume of 31 000 L, how many kilograms of hydrogen were needed to fill the balloon at STP?
<IMAGE>
A weather balloon is partially filled with helium to allow for expansion at high altitudes. At STP, a weather balloon is filled with enough helium to give a volume of 25.0 L. At an altitude of 30.0 km and –35 ⁰C, it has expanded to 2460 L. The increase in volume causes it to burst and a small parachute returns the instruments to Earth.
b. What is the final pressure, in millimeters of mercury, of the helium inside the balloon when it bursts?