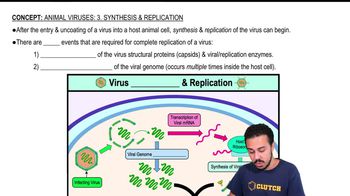
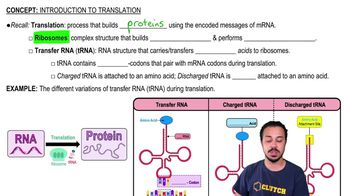
In Griffith's classical experiments on transformation, which of the following scenarios led to a dead mouse? Select all that apply.
a. Infecting the mouse with a living strain of S. pneumoniae that makes a capsule
b. Infecting the mouse with a heat-killed strain of S. pneumoniae that makes a capsule
c. Infecting the mouse with a heat-killed strain of S. pneumoniae that makes a capsule and a living strain of S. pneumoniae that cannot make a capsule
d. Infecting the mouse with a living strain of S. pneumoniae that cannot make a capsule