Back
BackProblem 1
A Salmonella species is grown for 8 hours. In this time, each cell divides about four times. What is the generation time?
Problem 2
If a bacterium that normally lives in the gastrointestinal tract is plunged into a salty solution, what would occur?
a. Halophilic adjustment
b. Osmotic concentration
c. Lysis
d. Plasmolysis
e. Nothing
Problem 3
After performing the streak plate method, what feature(s) would you look for on the agar plate to determine if you have a pure culture?
Problem 4
Which of the following pathogens would hyperbaric oxygen therapy, a treatment that increases the level of dissolved oxygen in tissues, most likely ward off? Select all that apply.
a. Anaerobic thermophile
b. Anaerobic mesophile
c. Facultative anaerobic thermophile
d. Facultative anaerobic mesophile
e. Microaerophilic mesophile
Problem 5
Choose the false statement about binary fission.
a. It generates genetically diverse daughter cells.
b. It is an asexual form of reproduction.
c. It is the most common way that prokaryotes divide.
d. It leads to exponential population growth.
e. If it occurs in a single plane, it could generate chains of bacteria.
Problem 6
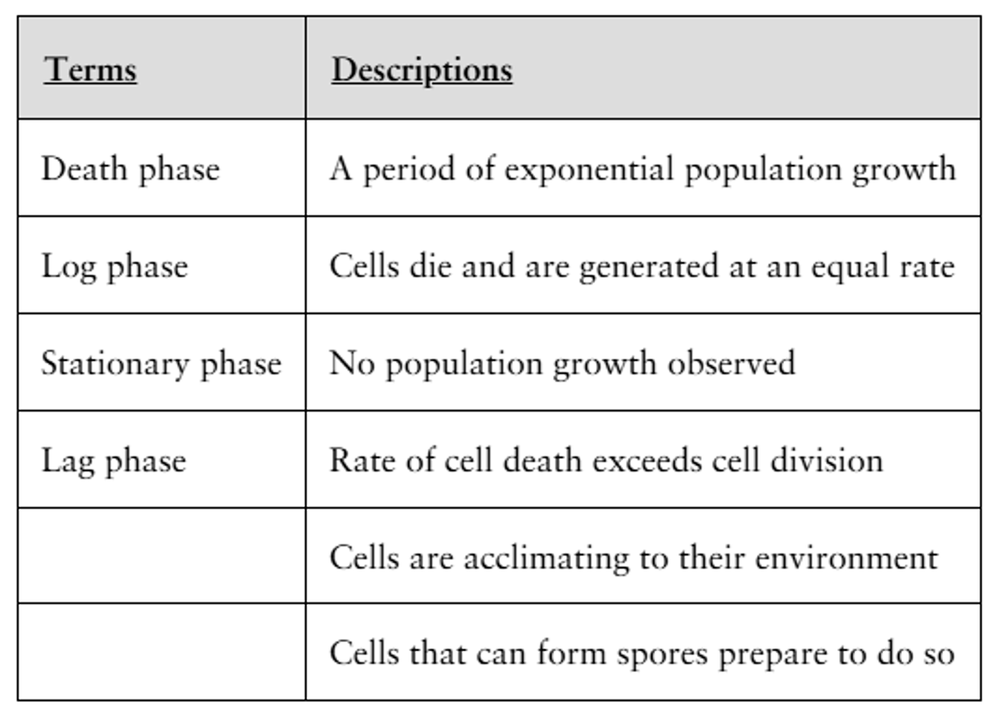
Match the term to the proper description(s). A term can have more than one description.
Problem 7
In a closed batch system, not all cells are expected to die, even as the death phase advances. Why?
Problem 8
Which direct enumeration method differentiates living from nonliving cells?
a. Manual cell counts
b. Measuring dry weight of cells
c. Viable plate count
d. Measuring biochemical activity
e. Coulter counter
Problem 9
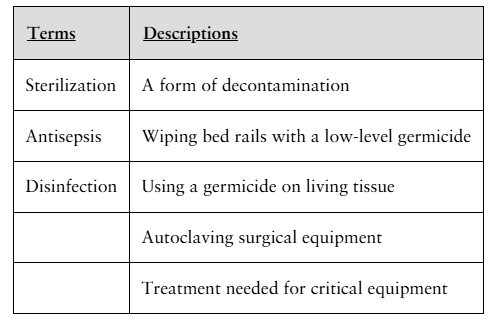
Match the term to the proper description(s). A term can have more than one description.
Problem 10
You are collecting a clinical sample for microbiological analysis. Which of the following is the most important thing you must do?
a. Follow aseptic protocols.
b. Refrigerate the samples immediately after collection.
c. Determine if the potential pathogen is an aerobe or strict anaerobe.
d. Determine if normal flora have been removed before the sample is collected.
Problem 11
Label each statement that follows as true or false, and correct the false statements so they are true:
a. Most pathogens would be considered mesophilic alkaliphiles.
b. Sterilization is a form of decontamination.
c. Disinfection is a form of decontamination.
d. High-level germicides achieve sterilization.
e. Ionizing radiation is a form of chemical microbial control.
f. Standard pasteurization is a way to sterilize milk.
Problem 12
You have a patient who is suffering from a Clostridioides difficile infection. Which of the following would most likely be recommended to decontaminate small heat-stable equipment used for the patient?
a. Autoclave all equipment at 121°C for 15 minutes.
b. Boil equipment for 3 minutes.
c. Place the equipment in a hot-air oven at 121°C for 15 minutes.
d. Treat all equipment with a detergent solution.
e. None of the above.
Problem 13
Choose the false statement about turbidity as an enumeration method.
a. It is an indirect enumeration method.
b. It is performed using a spectrophotometer.
c. It must be done using a liquid culture.
d. It differentiates between live and dead cells.
e. It is a rapid enumeration method.
Problem 14
_____________ microbes use oxygen in metabolism, while _____________ do not.
Problem 15
If you were a manufacturer of electronic pacemakers for heart implantation, which agent would you most likely use to treat your product?
a. Ethanol
b. Iodophor
c. Glutaraldehyde
d. Autoclave
e. Ethylene oxide
Problem 16
You are collecting a sample from a deep wound for analysis by the clinical microbiology lab. Which of the following is not a consideration as you undertake this process?
a. Avoiding the skin as the wound is swabbed
b. Using an anaerobic culture tube
c. Disinfecting the tube before collecting the sample
d. Washing your hands before and after sample collection
e. Using complex media
Problem 17
The _____________ is the time needed to kill 90 percent of a given microbial population at a set temperature. The _____________ is the lowest temperature needed to kill all microbes in a sample within 10 minutes.
Problem 18
Which of the following is (are) true? Select all that apply.
a. Scalpels are critical equipment.
b. Endoscopes are noncritical equipment.
c. Stethoscopes are noncritical equipment.
d. Anesthesia tubing is semicritical equipment.
e. Critical equipment contacts intact skin.
Problem 19
A bacterial specimen exhibits the following growth on blood agar. What can you most reasonably conclude about the bacterium? Select all that apply.
a. It is not S. pyogenes.
b. It is alpha hemolytic.
c. It is beta hemolytic.
d. It is gamma hemolytic.
e. It is Gram-positive.
<Image>
Problem 20
While hiking, Huda wants to ensure that the river water is clean enough to drink and will not cause any intestinal infections. How could she treat water from a stream so that it is safe to drink?