Back
BackProblem 1
Which of the following organisms are most closely related? Are any two the same species? On what did you base your answer?
Problem 2
Here is some additional information on the organisms in question 1:
Which of these organisms are most closely related? Compare this answer with your response to review question 1.
Problem 3
DRAW IT Use the following rRNA information to construct a cladogram for some of the organisms used in question 4. What is the purpose of a cladogram? How does your cladogram differ from a dichotomous key for these organisms?
Problem 4
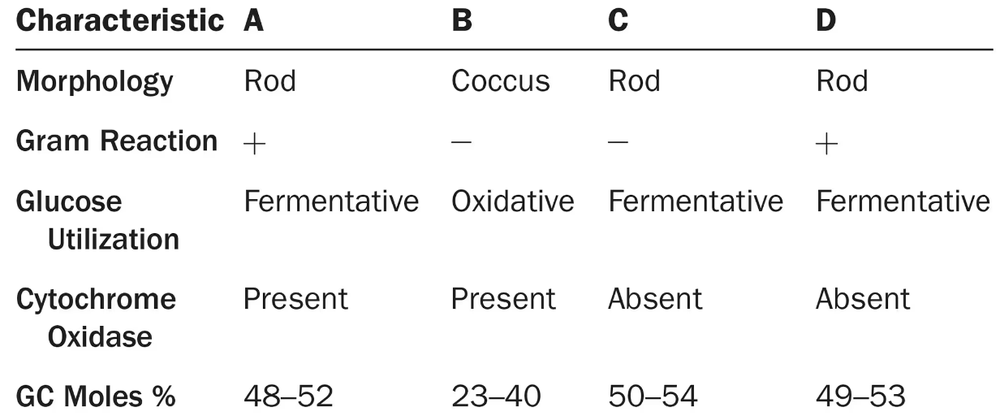
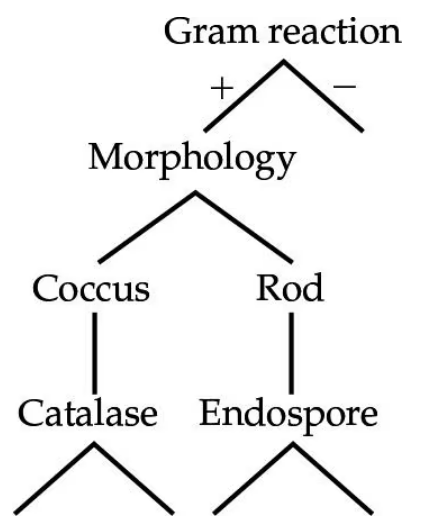
Use the information in the following table to complete the dichotomous key to these organisms. What is the purpose of a dichotomous key? Look up each genus in Chapter 11, and provide an example of why this organism is of interest to humans.
Problem 5
Use the key in the Clinical Focus box to identify the gram-negative, oxidase-positive rod causing pneumonia in a sea otter. It is H2S-positive, indole-negative, and urease-positive.
Problem 1
Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria differs from Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former
a. Groups bacteria into species
b. Groups bacteria according to phylogenetic relationships
c. Groups bacteria according to pathogenic properties
d. Groups bacteria into 19 species
e. All of the above
Problem 2
Bacillus and Lactobacillus are not in the same order. This indicates that which one of the following is not sufficient to assign an organism to a taxon?
a. Biochemical characteristics
b. Amino acid sequencing
c. Phage typing
d. Serology
e. Morphological characteristics
Problem 3
Which of the following is used to classify organisms into the Kingdom Fungi?
a. Ability to photosynthesize; possess a cell wall
b. Unicellular; possess cell wall; prokaryotic
c. Unicellular; lacking cell wall; eukaryotic
d. Absorptive; possess cell wall; eukaryotic
e. Ingestive; lacking cell wall; multicellular; prokaryotic
Problem 4
Which of the following is false about scientific nomenclature?
a. Each name is specific.
b. Names vary with geographical location.
c. The names are standardized.
d. Each name consists of a genus and specific epithet.
e. It was first designed by Linnaeus.
Problem 5
You could identify an unknown bacterium by all of the following except
a. hybridizing a DNA probe from a known bacterium with the unknown’s DNA.
b. making a fatty acid profile of the unknown.
c. specific antiserum agglutinating the unknown.
d. ribosomal RNA sequencing.
e. percentage of guanine + cytosine.
Problem 7
The wall-less mycoplasmas are considered to be related to gram-positive bacteria. Which of the following would provide the most compelling evidence for this?
a. They share common rRNA sequences.
b. Some gram-positive bacteria and some mycoplasmas produce catalase.
c. Both groups are prokaryotic.
d. Some gram-positive bacteria and some mycoplasmas have coccus-shaped cells.
e. Both groups contain human pathogens.
Problem 7
Use the following choices to answer questions 7 and 8.
a. Animalia
b. Fungi
c. Plantae
d. Bacillota (gram-positive bacteria)
e. Pseudomonadota (gram-negative bacteria)
Into which group would you place a multicellular organism that has a mouth and lives inside the human liver?
Problem 8
Use the following choices to answer questions 7 and 8.
a. Animalia
b. Fungi
c. Plantae
d. Bacillota (gram-positive bacteria)
e. Pseudomonadota (gram-negative bacteria)
Into which group would you place a photosynthetic organism that lacks a nucleus and has a thin peptidoglycan wall surrounded by an outer membrane?
Problem 9
Use the following choices to answer questions 9 and 10.
1. 9 + 2 flagella
2. 70s ribosome
3. fimbria
4. nucleus
5. peptidoglycan
6. plasma membrane
Which is (are) found in all three domains?
a. 2,6
b. 5
c. 2,4,6
d. 1,3,5
e. all six
Problem 10
Use the following choices to answer questions 9 and 10.
1. 9 + 2 flagella
2. 70s ribosome
3. fimbria
4. nucleus
5. peptidoglycan
6. plasma membrane
Which is (are) found only in prokaryotes?
a. 1,4,6
b. 3,5
c. 1,2
d. 4
e. 2,4,5