A large hospital washes burn patients in a stainless steel tub. After each patient, the tub is cleaned with a quat. It was noticed that 14 of 20 burn patients acquired Pseudomonas infections after being bathed. Provide an explanation for this high rate of infection.
Ch. 7 - The Control of Microbial Growth

Tortora14th EditionMicrobiology: An IntroductionISBN: 9780138200398Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 7, Problem 10
Which of the following is most likely to be bactericidal?
a. Membrane filtration
b. Ionizing radiation
c. Lyophilization (freeze-drying)
d. Deep-freezing
e. All of the above
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the meaning of 'bactericidal'—it refers to agents or processes that kill bacteria, as opposed to 'bacteriostatic,' which only inhibit bacterial growth without killing them.
Step 2: Analyze each option in terms of its effect on bacteria: membrane filtration physically removes bacteria but does not kill them; ionizing radiation damages bacterial DNA and cellular components, leading to bacterial death; lyophilization (freeze-drying) removes water to preserve bacteria but does not kill them; deep-freezing slows bacterial metabolism but generally does not kill bacteria.
Step 3: Recognize that ionizing radiation is known to cause lethal damage to bacteria by breaking DNA strands and generating reactive molecules, making it bactericidal.
Step 4: Compare the other methods to ionizing radiation and note that they are primarily bacteriostatic or preservation techniques rather than bactericidal.
Step 5: Conclude that among the options, ionizing radiation is the most likely to be bactericidal.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Bactericidal vs. Bacteriostatic Agents
Bactericidal agents kill bacteria outright, whereas bacteriostatic agents inhibit bacterial growth without killing them. Understanding this distinction helps determine which methods actively destroy bacteria versus those that merely preserve or inhibit them.
Recommended video:
Guided course
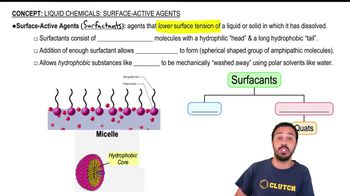
Liquid Chemicals: Surface-Active Agents
Ionizing Radiation as a Microbial Control Method
Ionizing radiation, such as gamma rays or X-rays, damages bacterial DNA and cellular components, leading to cell death. It is a potent bactericidal method commonly used for sterilization of medical equipment and food products.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Physical Methods to Control Microbial Growth
Physical Methods of Microbial Control: Filtration, Freeze-Drying, and Freezing
Membrane filtration physically removes bacteria but does not kill them. Lyophilization (freeze-drying) and deep-freezing preserve bacteria by halting metabolic activity but are generally bacteriostatic, not bactericidal, as they do not destroy bacterial cells.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Physical Methods to Control Microbial Growth
Related Practice
Textbook Question
517
views
Textbook Question
You and your classmates are trying to determine how a disinfectant might kill cells. You observe that when you spill the disinfectant in a tube of reduced litmus milk, the litmus turns blue again. You suggest to your classmates that:
a. The disinfectant might inhibit cell wall synthesis
b. The disinfectant might oxidize molecules
c. The disinfectant might inhibit protein synthesis
d. The disinfectant might denature proteins
e. The disinfectant might damage DNA
639
views
Textbook Question
What bacteria have porins, are resistant to bisphenols, and survive and may grow in quats?
534
views
