An air-track glider attached to a spring oscillates with a period of 1.5 s. At t = 0 s the glider is 5.00 cm left of the equilibrium position and moving to the right at 36.3 cm/s. What is the phase constant?

A block attached to a spring with unknown spring constant oscillates with a period of 2.0 s. What is the period if The spring constant is doubled? Parts a to d are independent questions, each referring to the initial situation.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)

Period of Oscillation
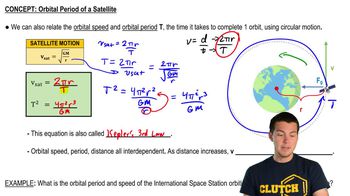
Effect of Spring Constant on Period

A 200 g air-track glider is attached to a spring. The glider is pushed in 10 cm and released. A student with a stopwatch finds that 10 oscillations take 12.0 s. What is the spring constant?
A block attached to a spring with unknown spring constant oscillates with a period of 2.0 s. What is the period if the amplitude is doubled?
A 200 g mass attached to a horizontal spring oscillates at a frequency of 2.0 Hz. At t = 0 s, the mass is at x = 5.0 cm and has vx = -30 cm/s. Determine: The maximum speed.
A 200 g mass attached to a horizontal spring oscillates at a frequency of 2.0 Hz. At t = 0 s, the mass is at x = 5.0 cm and has vₓ = -30 cm/s. Determine: The total energy.
A 200 g mass attached to a horizontal spring oscillates at a frequency of 2.0 Hz. At t = 0 s, the mass is at x = 5.0 cm and has vx = -30 cm/s. Determine: The position at t = 0.40 s.
