Textbook Question
Sketch the shape and orientation of the following types of orbitals: (a) px, (b) dz2, (c) dx2 - y2.
533
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


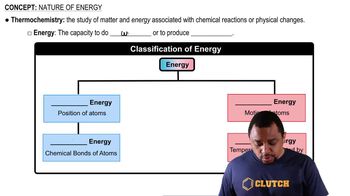
Sketch the shape and orientation of the following types of orbitals: (a) px, (b) dz2, (c) dx2 - y2.
(c) What can you say about the average distance from the nucleus of an electron in a 2s orbital as compared with a 3s orbital?
(a) With reference to Figure 6.19, what is the relationship between the number of nodes in an s orbital and the value of the principal quantum number?
(b) Identify the number of nodes; that is, identify places where the electron density is zero, in the 2px orbital; in the 3s orbital.
(d) For the hydrogen atom, list the following orbitals in order of increasing energy: 3s, 2s, 2p, 5s, 4d.