Define and discuss these terms:
(a) synapsis
(b) bivalents
(c) chiasmata
(d) crossing over
(e) chromomeres
(f) sister chromatids
(g) tetrads
(h) dyad
(i) monads

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
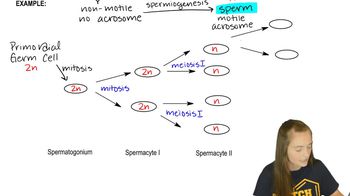


Define and discuss these terms:
(a) synapsis
(b) bivalents
(c) chiasmata
(d) crossing over
(e) chromomeres
(f) sister chromatids
(g) tetrads
(h) dyad
(i) monads
Contrast the genetic content and the origin of sister versus nonsister chromatids during their earliest appearance in prophase I of meiosis. How might the genetic content of these change by the time tetrads have aligned at the equatorial plate during metaphase I?
Given the end results of the two types of division, why is it necessary for homologs to pair during meiosis and not desirable for them to pair during mitosis?
A diploid cell contains three pairs of homologous chromosomes designated C1 and C2, M1 and M2, and S1 and S2. No crossing over occurs. What combinations of chromosomes are possible in?
(a) daughter cells following mitosis
(b) cells undergoing the first meiotic metaphase
(c) haploid cells following both divisions of meiosis
Considering Problem 15, predict the number of different haploid cells that could be produced by meiosis if a fourth chromosome pair (W1 and W2) were added.