Textbook Question
How do we know that microRNAs negatively regulate target mRNAs?
594
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



How do we know that microRNAs negatively regulate target mRNAs?
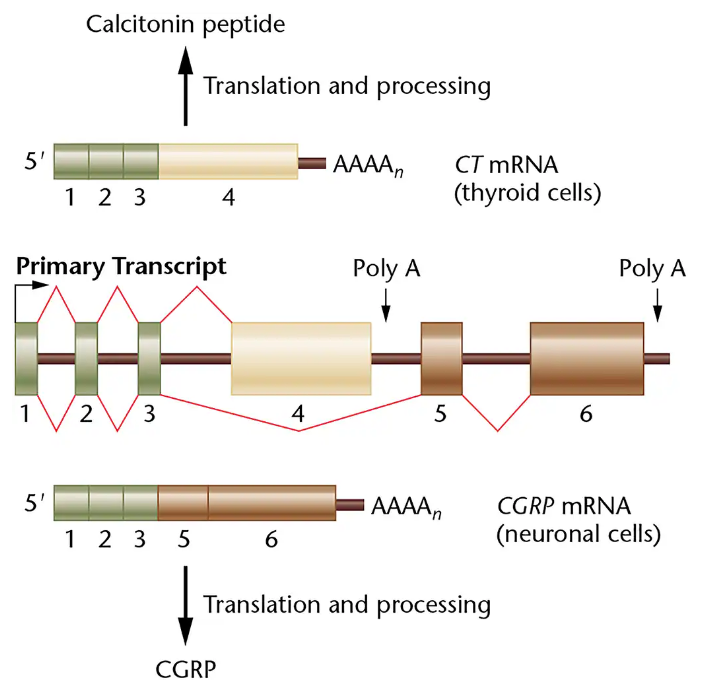
Write a short essay describing how an mRNA may be regulated in three different ways by specific cis-elements and RBPs.
List three types of alternative splicing patterns and how they lead to the production of different protein isoforms.
Explain how the use of alternative promoters and alternative polyadenylation signals produces mRNAs with different 5' and 3' ends.
Explain how a tissue-specific RNA-binding protein can lead to tissue-specific alternative splicing via splicing enhancers or splicing silencers.
The regulation of mRNA decay relies heavily upon deadenylases and decapping enzymes. Explain how these classes of enzymes are critical to initiating mRNA decay.