Textbook Question
What is the phenotype associated with zygotic gene mutations?
628
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
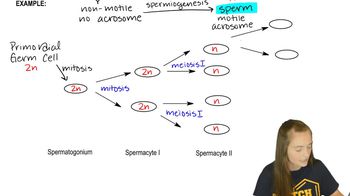


What is the phenotype associated with zygotic gene mutations?
Does the maternal genotype contain zygotic genes?
List the main classes of zygotic genes. What is the function of each class of these genes?
How can you determine whether a particular gene is being transcribed in different cell types?
You observe that a particular gene is being transcribed during development. How can you tell whether the expression of this gene is under transcriptional or translational control?
The homeotic mutation Antennapedia causes mutant Drosophila to have legs in place of antennae and is a dominant gain-of-function mutation. What are the properties of such mutations? How does the Antennapedia gene change antennae into legs?