Identify each of the following as a nucleoside or a nucleotide:
d. cytidine monophosphate

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

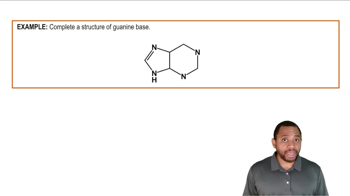
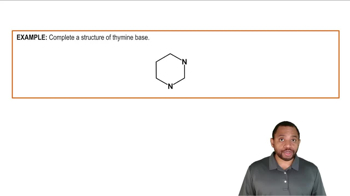
Identify each of the following as a nucleoside or a nucleotide:
d. cytidine monophosphate
Identify each of the following as a nucleoside or a nucleotide:
b. guanosine
State whether each of the following components is present in DNA only, RNA only, or both DNA and RNA:
c. deoxycytidine monophosphate
In the genetic disease uridine monophosphate synthase deficiency, symptoms include anemia, cardiac malformations, and infections. Draw the condensed structural formula for uridine monophosphate.
A deficiency of the enzyme adenine transferase causes a lack of adenine for purine synthesis and a high level of adenine in the urine. Draw the condensed structural formula for adenosine monophosphate.
What nucleic acid subunits are connected in a phosphodiester linkage in a polynucleotide?