Textbook Question
Identify each of the following bases as a purine or a pyrimidine:
b.
859
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
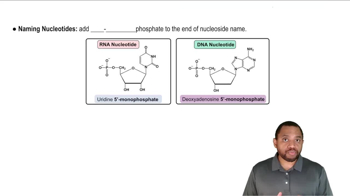


Identify each of the following bases as a purine or a pyrimidine:
b.
Identify each of the following bases as a purine or a pyrimidine:
a. guanine
Identify each of the following as a nucleoside or a nucleotide:
b. deoxycytidine
Identify each of the following as a nucleoside or a nucleotide:
b. guanosine
State whether each of the following components is present in DNA only, RNA only, or both DNA and RNA:
c. deoxycytidine monophosphate
State whether each of the following components is present in DNA only, RNA only, or both DNA and RNA:
c. uracil