Determine each of the following for a 0.050 M KOH solution:
b. pH

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

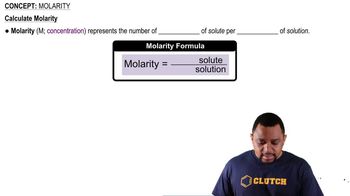

Determine each of the following for a 0.050 M KOH solution:
b. pH
Determine each of the following for a 0.100 M HBr solution:
a. [H3O+]
Determine each of the following for a 0.100 M HBr solution:
b. pH
One of the most acidic lakes in the United States is Little Echo Pond in the Adirondacks in New York. Recently, this lake had a pH of 4.2, well below the recommended pH of 6.5.
a. What are the [H3O+] and [OH-] of Little Echo Pond?
One of the most acidic lakes in the United States is Little Echo Pond in the Adirondacks in New York. Recently, this lake had a pH of 4.2, well below the recommended pH of 6.5.
c. One way to raise the pH (and restore aquatic life) is to add limestone (CaCO3). How many grams of CaCO3 are needed to neutralize 1.0 kL of the acidic water from Little Echo Pond if the acid is sulfuric acid?
H2SO4(aq) + CaCO3(s) → CO2(g) + H2O(l) + CaSO4(aq)
The daily output of stomach acid (gastric juice) is 1000 mL to 2000 mL. Prior to a meal, stomach acid (HCl) typically has a pH of 1.42.
c. The antacid milk of magnesia contains 400. mg of Mg(OH)2 per teaspoon. Write the neutralization equation, and calculate the number of milliliters of stomach acid neutralized by 1 tablespoon of milk of magnesia (1tablespoon = 3teaspoons).