Textbook Question
Identify the reactant that is a Brønsted–Lowry acid and the reactant that is a Brønsted–Lowry base in each of the following:
a. HI(aq) + H2O(l) → I-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
731
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
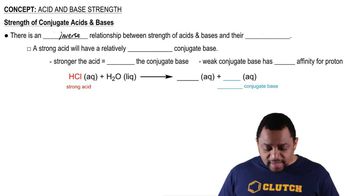


Identify the reactant that is a Brønsted–Lowry acid and the reactant that is a Brønsted–Lowry base in each of the following:
a. HI(aq) + H2O(l) → I-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
Write the formula for the conjugate base for each of the following acids:
b. H2O
Write the formula for the conjugate base for each of the following acids:
a. HCO3-
Write the formula for the conjugate acid for each of the following bases:
a. CO32-
Write the formula for the conjugate acid for each of the following bases:
c. H2PO4-
Identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base pairs in each of the following equations:
b. NH4+(aq) + H2O(l) ⇄ NH3(aq) + H3O+(aq)