Textbook Question
Identify each of the following properties as more typical of an organic or inorganic compound:
c. contains carbon and hydrogen
1102
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


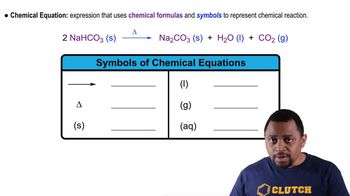
Identify each of the following properties as more typical of an organic or inorganic compound:
c. contains carbon and hydrogen
Identify each of the following properties as more typical of an organic or inorganic compound:
b. is a gas at room temperature
Identify each of the following properties as more typical of an organic or inorganic compound:
c. contains covalent bonds
Match each of the following physical and chemical properties with ethane, C2H6 or sodium bromide, NaBr:
b. burns vigorously in air
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alkanes and cycloalkanes:
a. <IMAGE>
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alkanes and cycloalkanes:
c.