Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
<IMAGE>
b. Write the balanced chemical equation for the formation of propyl acetate.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
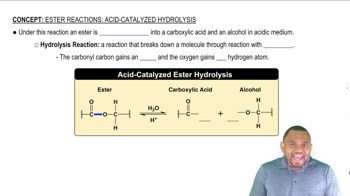


Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
<IMAGE>
b. Write the balanced chemical equation for the formation of propyl acetate.
Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
<IMAGE>
d. Write the balanced chemical equation for the base hydrolysis of propyl acetate with NaOH.
Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
<IMAGE>
e. How many milliliters of a 0.208 M NaOH solution is needed to completely hydrolyze (saponify) 1.58 g of propyl acetate?
Ethyl octanoate is a flavor component of mangoes.
<IMAGE>
e. How many milliliters of a 0.315 M NaOH solution is needed to completely hydrolyze (saponify) 2.84 g of ethyl octanoate?
Novocain, a local anesthetic, is the ammonium salt of procaine.
a. Draw the condensed structural formula for the ammonium salt (procaine hydrochloride) formed when procaine reacts with HCl. (Hint: The tertiary amine reacts with HCl.)
Novocain, a local anesthetic, is the ammonium salt of procaine.
b. Why is procaine hydrochloride used rather than procaine?