Textbook Question
How does the double bond influence the dispersion forces that can form between the hydrocarbon chains of fatty acids?
718
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
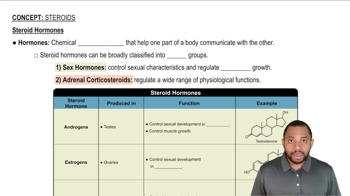
How does the double bond influence the dispersion forces that can form between the hydrocarbon chains of fatty acids?
Compare the structures and functional groups of arachidonic acid and prostaglandin PGE1.
What are some effects of prostaglandins in the body?
What is the difference in the location of the first double bond in an omega-3 and an omega-6 fatty acid (see Chemistry Link to Health “Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Fish Oils”)?
Draw the condensed structural formula for the ester in jojoba wax that is formed from arachidic acid, a 20-carbon saturated fatty acid, and 1-docosanol, CH3–(CH2)21–OH.
Draw the condensed structural formula for a triacylglycerol that contains stearic acid and glycerol.