Textbook Question
Compare the structures and functional groups of arachidonic acid and prostaglandin PGE1.
685
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
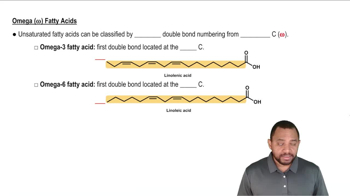


Compare the structures and functional groups of arachidonic acid and prostaglandin PGE1.
What are some effects of prostaglandins in the body?
How does an anti-inflammatory drug reduce inflammation?
Draw the condensed structural formula for the ester in jojoba wax that is formed from arachidic acid, a 20-carbon saturated fatty acid, and 1-docosanol, CH3–(CH2)21–OH.
Draw the condensed structural formula for a triacylglycerol that contains stearic acid and glycerol.
Draw the condensed structural formula for a mixed triacylglycerol that contains two palmitic acid molecules and one oleic acid molecule on the center carbon of glycerol.