Textbook Question
Draw the structure for cholesterol.
1428
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
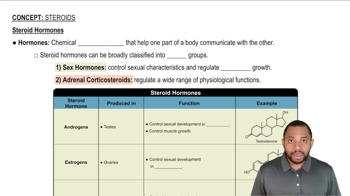


Draw the structure for cholesterol.
How do chylomicrons differ from VLDL?
Why is LDL called “bad” cholesterol?
What is the function of the lipid bilayer in a cell membrane?
How do molecules of cholesterol affect the structure of cell membranes?
Where are proteins located in cell membranes?