Textbook Question
What is the name of the class of enzymes that would catalyze each of the following reactions?
c. splitting peptide bonds in proteins
1082
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


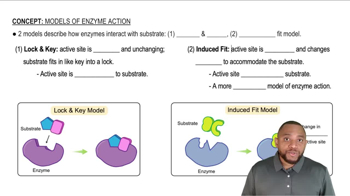
What is the name of the class of enzymes that would catalyze each of the following reactions?
c. splitting peptide bonds in proteins
Match the terms (1) enzyme–substrate complex, (2) enzyme, and (3) substrate with each of the following:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
Match the terms (1) enzyme–substrate complex, (2) enzyme, and (3) substrate with each of the following:
b. the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
Write an equation that represents an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
How is the active site different from the whole enzyme structure?
After the products have formed, what happens to the enzyme?