Textbook Question
Classify each of the following proteins according to its function:
a. hemoglobin, oxygen carrier in the blood
662
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

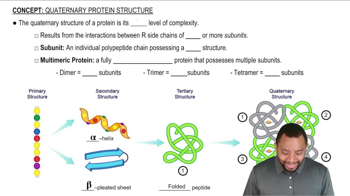
Classify each of the following proteins according to its function:
a. hemoglobin, oxygen carrier in the blood
Classify each of the following proteins according to its function:
a. insulin, a protein needed for glucose utilization
Classify each of the following proteins according to its function:
c. casein, milk protein
How does the polarity of the R group in leucine compare to the R group in serine?