Trypsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes polypeptides, functions in the small intestine at an optimum pH of 7.7 to 8.0. How is the rate of a trypsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
a. changing the pH to 3.0

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


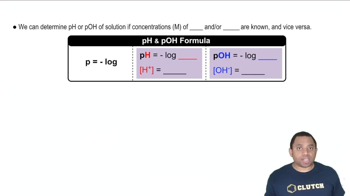
Trypsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes polypeptides, functions in the small intestine at an optimum pH of 7.7 to 8.0. How is the rate of a trypsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
a. changing the pH to 3.0
Trypsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes polypeptides, functions in the small intestine at an optimum pH of 7.7 to 8.0. How is the rate of a trypsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
b. running the reaction at 75 °C
Pepsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes proteins, functions in the stomach at an optimum pH of 1.5 to 2.0. How is the rate of a pepsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
a. changing the pH to 5.0
Refer to the graph in problem 16.45 to determine if the reaction rate in each condition will be at the optimum rate or not.
<IMAGE>
a. trypsin, pH 5.0
Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive enzyme inhibitor:
a. The inhibitor has a structure similar to the substrate.
Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive enzyme inhibitor:
d. The structure of the inhibitor is not similar to the substrate.