Textbook Question
Why are there at least 20 different tRNAs?
1474
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
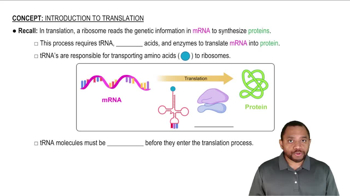


Why are there at least 20 different tRNAs?
What are the three steps of translation?
Where does protein synthesis take place?
Use three-letter and one-letter abbreviations to write the amino acid sequence for the peptide from each of the following mRNA sequences:
c. UAC GGG AGA UGU
Use three-letter and one-letter abbreviations to write the amino acid sequence for the peptide from each of the following mRNA sequences:
c. AUG CAC AAG GAA GUA CUG
The following sequence is a portion of the DNA template strand: TGT GGG GTT ATT
b. What are the anticodons of the tRNAs?