Use three-letter and one-letter abbreviations to write the amino acid sequence for the peptide from each of the following mRNA sequences:
a. ACC ACA ACU

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
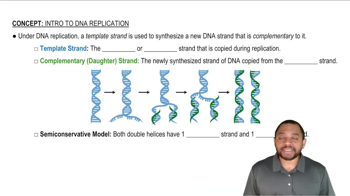
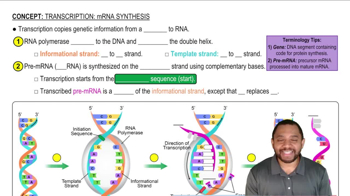
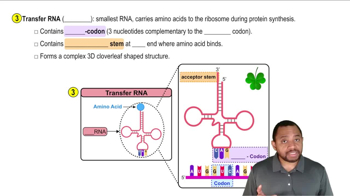
Use three-letter and one-letter abbreviations to write the amino acid sequence for the peptide from each of the following mRNA sequences:
a. ACC ACA ACU
Use three-letter and one-letter abbreviations to write the amino acid sequence for the peptide from each of the following mRNA sequences:
c. UAC GGG AGA UGU
Use three-letter and one-letter abbreviations to write the amino acid sequence for the peptide from each of the following mRNA sequences:
c. AUG CAC AAG GAA GUA CUG
The following is a segment of the DNA template that codes for human insulin: TTT GTG AAC CAA CAC CTG
b. Write the three-letter and one-letter abbreviations for this corresponding peptide segment.
What is the effect of a deletion mutation on the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide?
How is protein synthesis affected if the normal base sequence TTT in the DNA template strand is changed to TTC?