Textbook Question
How is ATP used in the initial steps of glycolysis?
1197
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
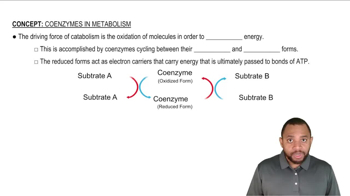
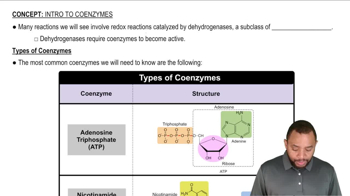
How is ATP used in the initial steps of glycolysis?
How many ATP or NADH are produced (or required) in each of the following steps in glycolysis?
a. glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
How many ATP or NADH are produced (or required) in each of the following steps in glycolysis?
c. phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate
How does the formation of lactate permit glycolysis to continue under anaerobic conditions?
What are the products from one turn of the citric acid cycle?
Identify the reaction(s) of the citric acid cycle that involve(s)
a. oxidation and decarboxylation