In a large building, oil is used in a steam boiler heating system. The combustion of 1.0 lb of oil provides 2.4 × 107 J.
a. How many kilograms of oil are needed to heat 150 kg of water from 22 °C to 100 °C?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


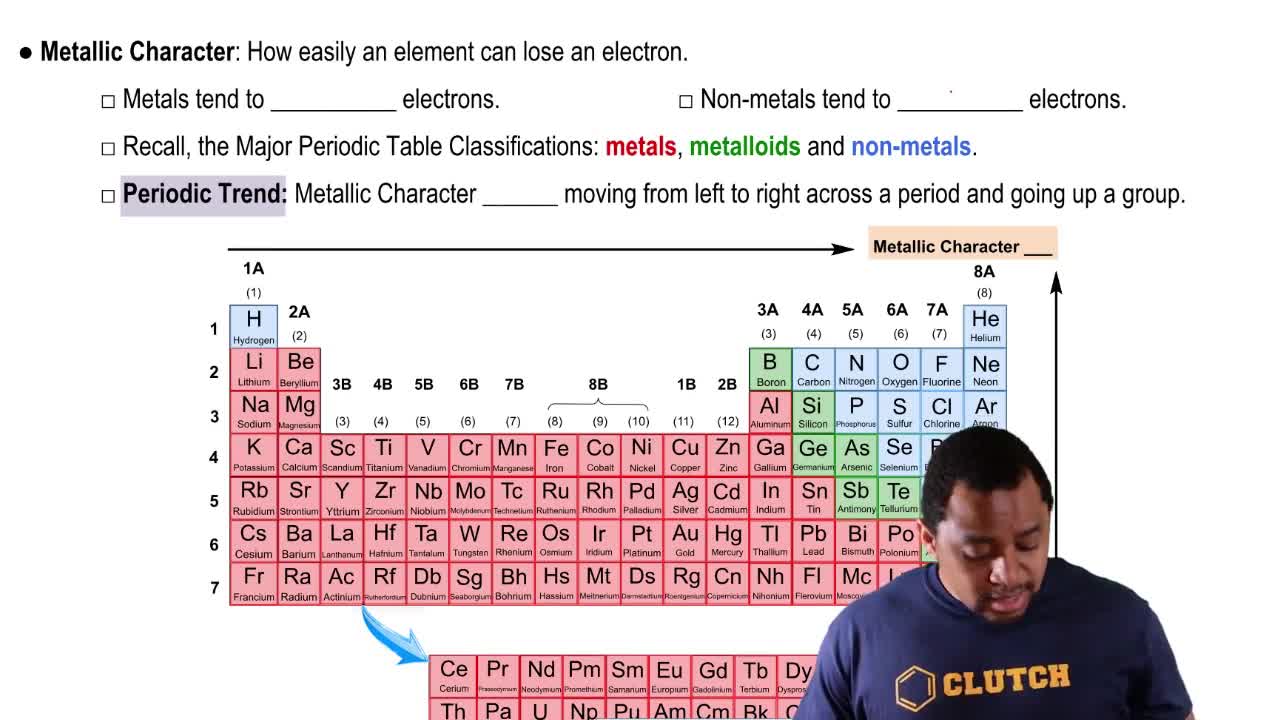
In a large building, oil is used in a steam boiler heating system. The combustion of 1.0 lb of oil provides 2.4 × 107 J.
a. How many kilograms of oil are needed to heat 150 kg of water from 22 °C to 100 °C?
In a large building, oil is used in a steam boiler heating system. The combustion of 1.0 lb of oil provides 2.4 × 107 J.
b. How many kilograms of oil are needed to change 150 kg of water to steam at 100 °C?
When 1.0 g of gasoline burns, it releases 11 kcal. The density of gasoline is 0.74 g/mL.
b. If a television requires 150 kJ/h to run, how many hours can the television run on the energy provided by 1.0 gal of gasoline?
A metal is thought to be copper or gold. When 18 g of the metal absorbs 58 cal, its temperature rises by 35 °C.
a. What is the specific heat, in cal/g °C, of the metal?